ChatGPT is taking the tech industry by storm, thanks to its unparalleled natural language processing capabilities. As a powerful AI language model, it has the ability to understand and generate human-like responses, revolutionizing communication in various industries. From streamlining customer service chatbots to enabling seamless language translation tools, ChatGPT has already proved its mettle in creating innovative solutions that improve efficiency and user experience.
Now the question is, can we leverage ChatGPT to transform the way we deliver applications? With the integration of ChatGPT into DevOps workflows, we are witnessing the possible emergence of a new era of automation called PromptOps. This advancement in AIOps technology is revolutionizing the way businesses operate, allowing for faster and more efficient application delivery.
In this article, we will explore how to integrate ChatGPT into your DevOps workflow to deliver applications.
Integrate ChatGPT into Your DevOps Workflow
When it comes to integrating ChatGPT into DevOps workflows, many developers are faced with the challenge of managing extra resources and writing complicated shells. However, there is a better way - KubeVela Workflow. This open-source cloud-native workflow project offers a streamlined solution that eliminates the need for pods or complex scripting.
In KubeVela Workflow, every step has a type that can be easily abstracted and reused. The step-type is programmed in CUE language, making it incredibly easy to customize and use atomic capabilities like a function call in every step. An important point to note is that with all these atomic capabilities, such as HTTP requests, it is possible to integrate ChatGPT in just 5 minutes by writing a new step.
Check out the Installation Guide to get started with KubeVela Workflow. The complete code of this
chat-gptstep type is available at GitHub.
Now that we choose the right tool, let's see the capabilities of ChatGPT in delivery.
Case 1: Diagnose the resources
It's quite common in the DevOps world to encounter problems like "I don't know why the pod is not running" or "I don't know why the service is not available". In this case, we can use ChatGPT to diagnose the resource.
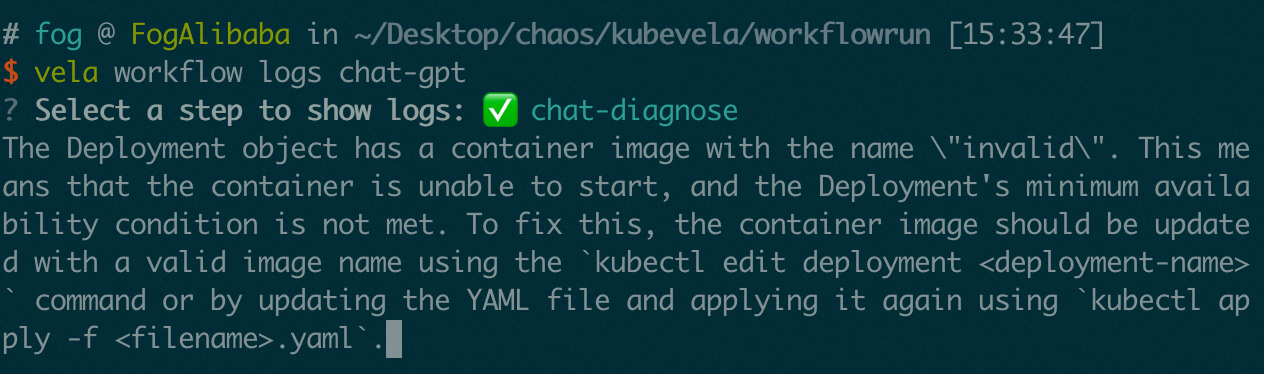
For example, In our workflow, we can apply a Deployment with an invalid image in the first step. Since the deployment will never be ready, we can add a timeout in the step to ensure the workflow is not stuck in this step. Then, passing the unhealthy resources deployed in the first step to the second step, we can use the chat-gpt step type to diagnose the resource to determine the issue. Note that the second step is only executed if the first one fails.
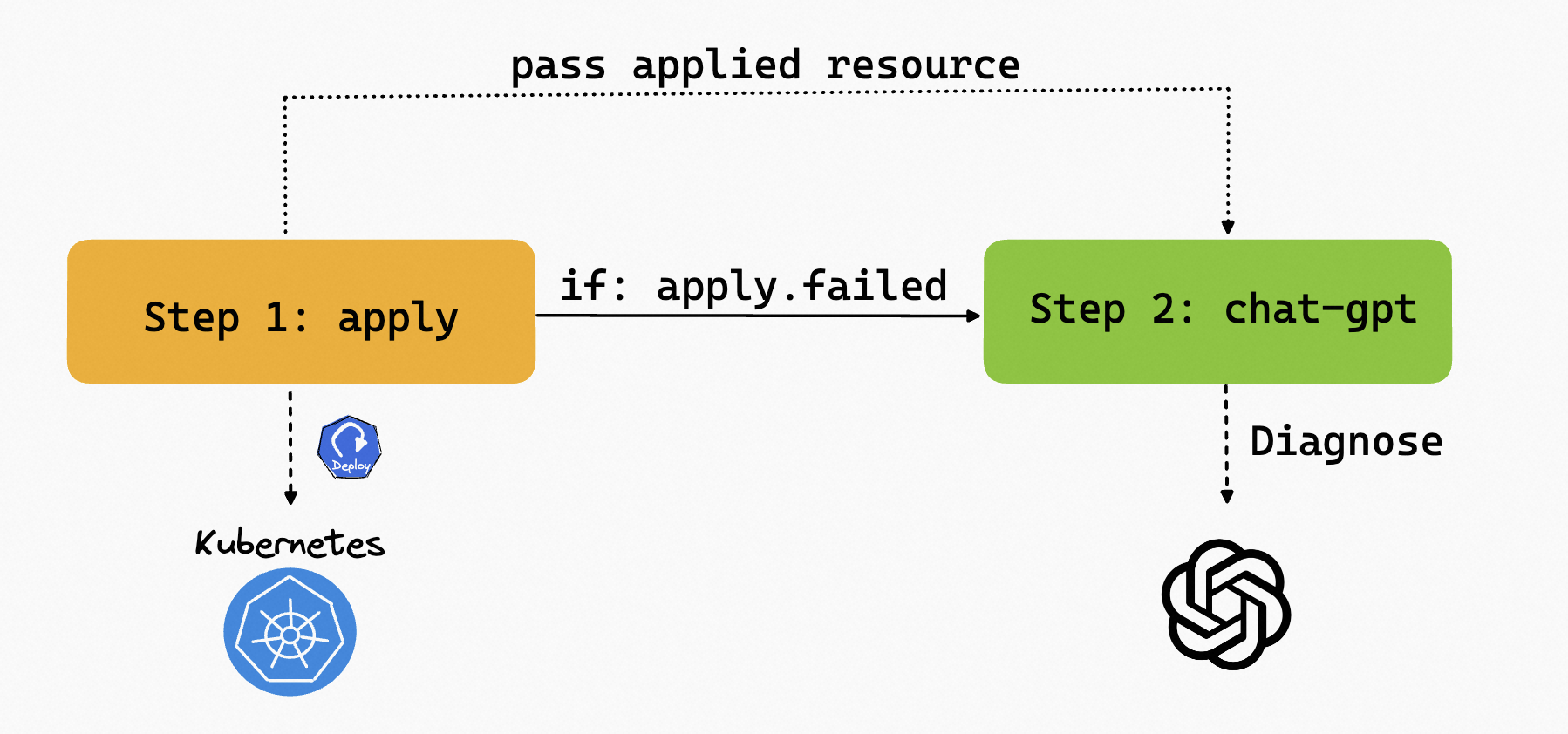
The complete workflow is shown below:
apiVersion: core.oam.dev/v1alpha1
kind: WorkflowRun
metadata:
name: chat-gpt-diagnose
namespace: default
spec:
workflowSpec:
steps:
# Apply an invalid deployment with a timeout
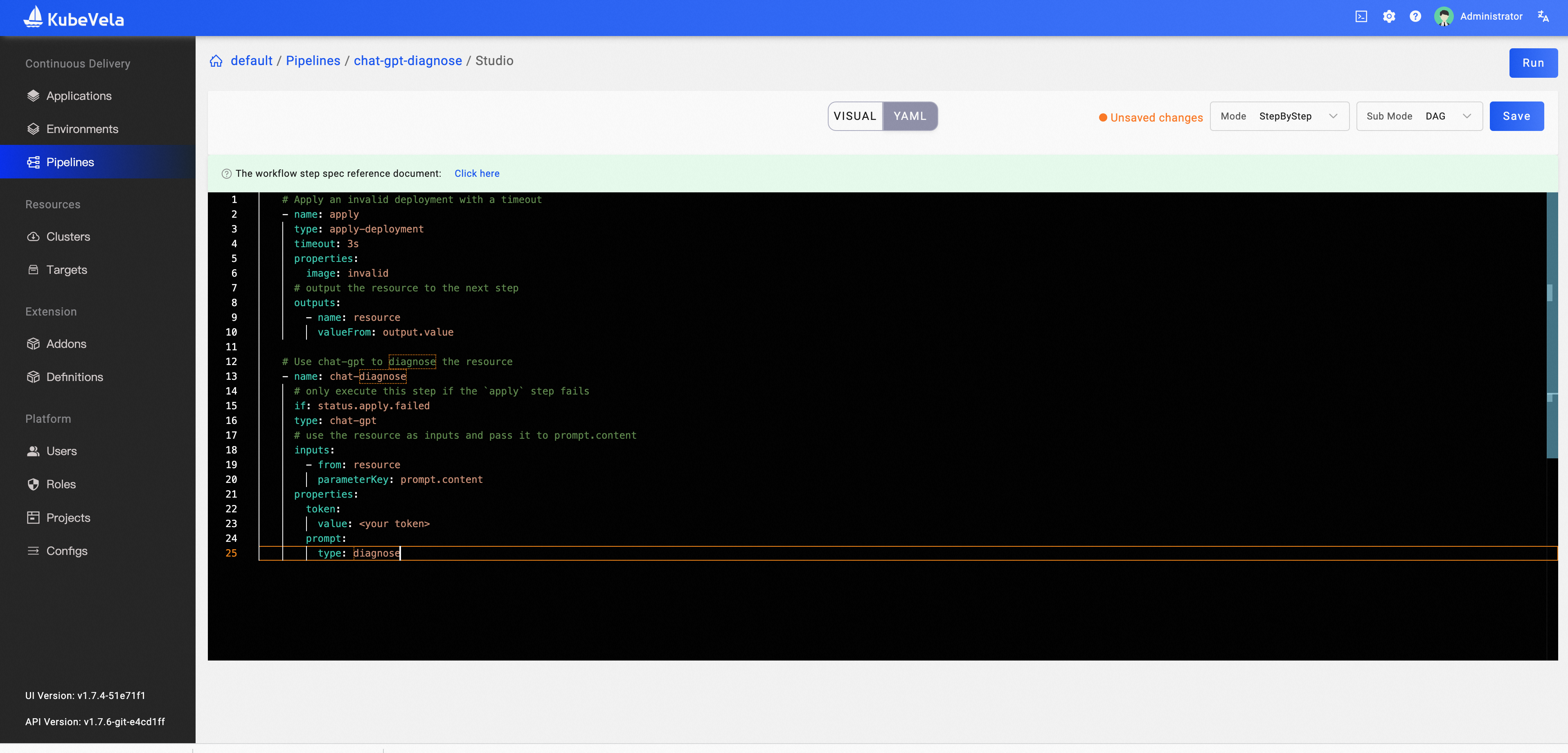
- name: apply
type: apply-deployment
timeout: 3s
properties:
image: invalid
# output the resource to the next step
outputs:
- name: resource
valueFrom: output.value
# Use chat-gpt to diagnose the resource
- name: chat-diagnose
# only execute this step if the `apply` step fails
if: status.apply.failed
type: chat-gpt
# use the resource as inputs and pass it to prompt.content
inputs:
- from: resource
parameterKey: prompt.content
properties:
token:
value: <your token>
prompt:
type: diagnose
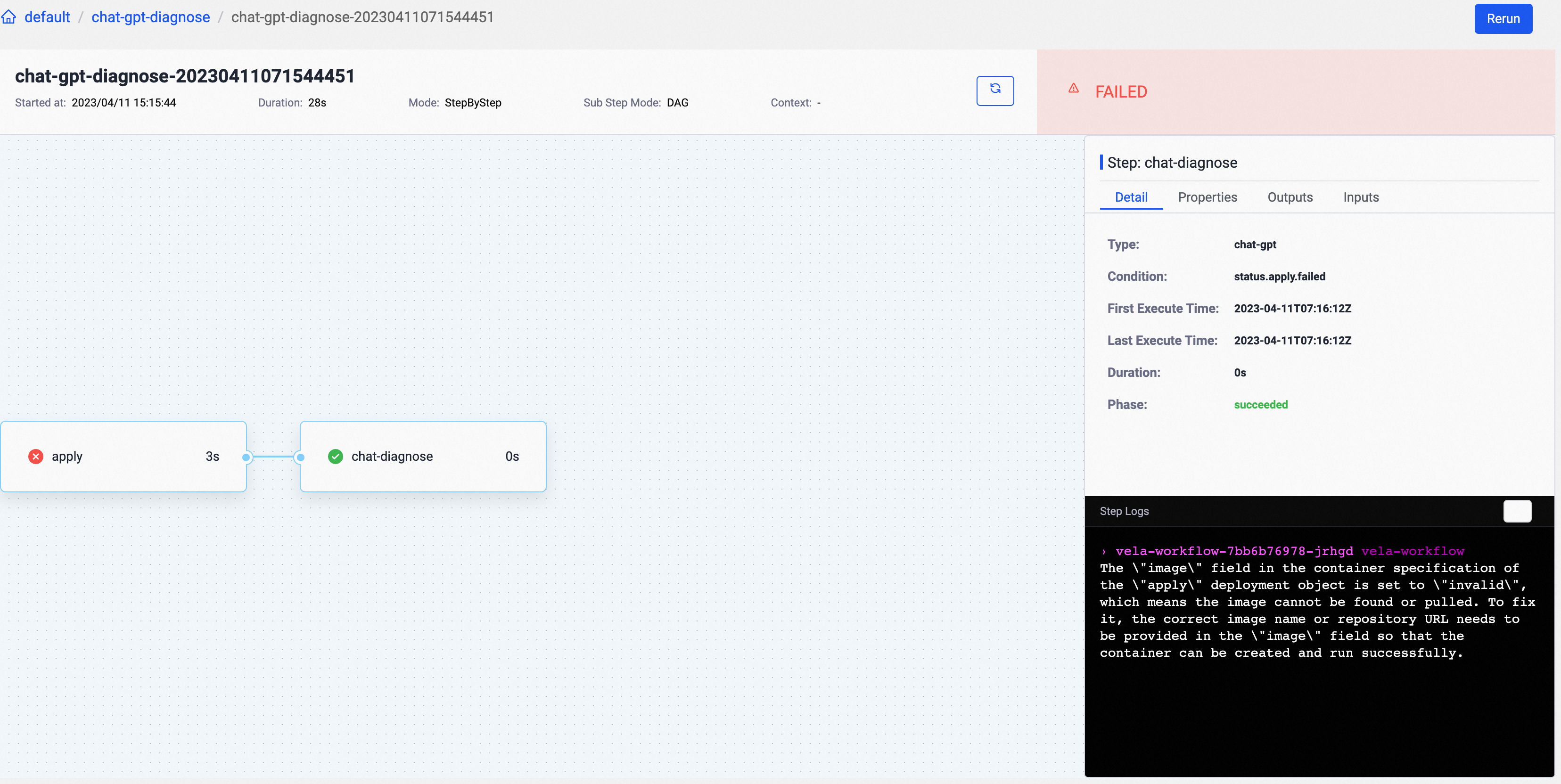
Apply this Workflow and check the result, the first step will fail because of timeout. Then the second step will be executed and the result of chat-gpt will be shown in the log:
vela workflow logs chat-gpt-diagnose
Visualize in the dashboard
If you want to visualize the process and the result in the dashboard, it's time to enable the [velaux](https://kubevela.io/docs/reference/addons/velaux#install) addon.
vela addon enable velaux
Copy all the steps in the above yaml to create a pipeline.
Run this pipeline, and you can check out the failed reason analyzed by ChatGPT in the logs of the second step.
Write the chat-gpt step from scratch
How to write this chat-gpt step type? Is it simple for you to write a step type like this? Let's see how to complete this step type.
We can first define what this step type need from the user. That is: the users' token for ChatGPT, and the resource to diagnose. For some other parameters like the model or the request timeout, we can set the default value with * like below:
parameter: {
token: value: string
// +usage=the model name
model: *"gpt-3.5-turbo" | string
// +usage=the prompt to use
prompt: {
type: *"diagnose" | string
lang: *"English" | string
content: {...}
}
timeout: *"30s" | string
}
Let's complete this step type by writing the logic of the step. We can first import vela/op package in which we can use the op.#HTTPDo capability to send a request to the ChatGPT API. If the request fails, the step should be failed with op.#Fail. We can also set this step's log data with ChatGPT's answer. The complete step type is shown below:
// import packages
import (
"vela/op"
"encoding/json"
)
// this is the name of the step type
"chat-gpt": {
description: "Send request to chat-gpt"
type: "workflow-step"
}
// this is the logic of the step type
template: {
// send http request to chat gpt
http: op.#HTTPDo & {
method: "POST"
url: "https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions"
request: {
timeout: parameter.timeout
body: json.Marshal({
model: parameter.model
messages: [{
if parameter.prompt.type == "diagnose" {
content: """
You are a professional kubernetes administrator.
Carefully read the provided information, being certain to spell out the diagnosis & reasoning, and don't skip any steps.
Answer in \(parameter.prompt.lang).
---
\(json.Marshal(parameter.prompt.content))
---
What is wrong with this object and how to fix it?
"""
}
role: "user"
}]
})
header: {
"Content-Type": "application/json"
"Authorization": "Bearer \(parameter.token.value)"
}
}
}
response: json.Unmarshal(http.response.body)
fail: op.#Steps & {
if http.response.statusCode >= 400 {
requestFail: op.#Fail & {
message: "\(http.response.statusCode): failed to request: \(response.error.message)"
}
}
}
result: response.choices[0].message.content
log: op.#Log & {
data: result
}
parameter: {
token: value: string
// +usage=the model name
model: *"gpt-3.5-turbo" | string
// +usage=the prompt to use
prompt: {
type: *"diagnose" | string
lang: *"English" | string
content: {...}
}
timeout: *"30s" | string
}
}
That's it! Apply this step type and we can use it in our Workflow like the above.
vela def apply chat-gpt.cue
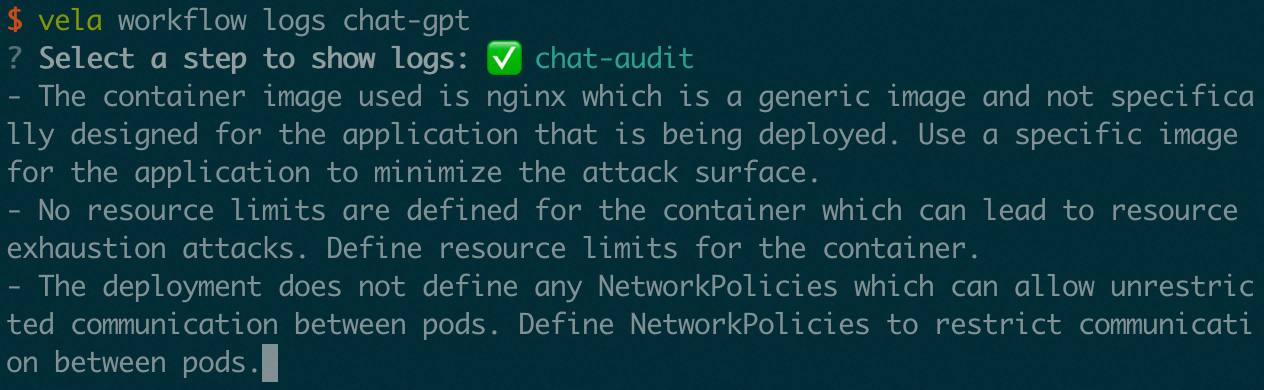
Case 2: Audit the resource
Now the ChatGPT is our Kubernetes expert and can diagnose the resource. Can it also give us some security advice for the resource? Definitely! It's just prompt. Let's modify the step type that we wrote in the previous case to add the audit feature. We can add a new prompt type audit and pass the resource to the prompt. You can check out the whole step type in GitHub.
In the Workflow, we can apply a Deployment with nginx image and pass it to the second step. The second step will use the audit prompt to audit the resource.
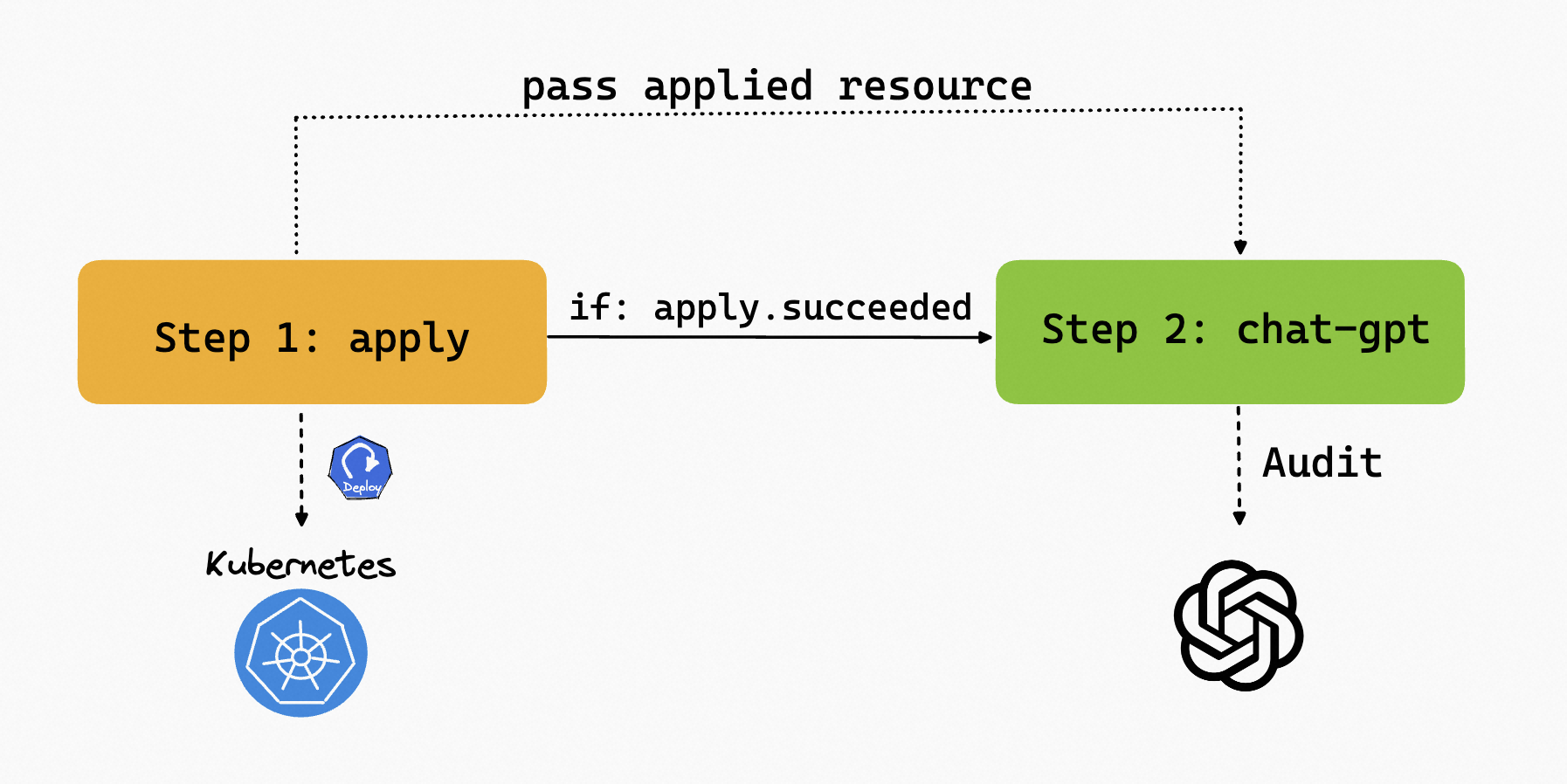 The complete Workflow is shown below:
The complete Workflow is shown below:
apiVersion: core.oam.dev/v1alpha1
kind: WorkflowRun
metadata:
name: chat-gpt-audit
namespace: default
spec:
workflowSpec:
steps:
- name: apply
type: apply-deployment
# output the resource to the next step
outputs:
- name: resource
valueFrom: output.value
properties:
image: nginx
- name: chat-audit
type: chat-gpt
# use the resource as inputs and pass it to prompt.content
inputs:
- from: resource
parameterKey: prompt.content
properties:
token:
value: <your token>
prompt:
type: audit
Use Diagnose & Audit in one Workflow
Now that we have the capability to diagnose and audit the resource, we can use them in one Workflow, and use the if condition to control the execution of the steps. For example, if the apply step fails, then diagnose the resource, if it succeeds, audit the resource.
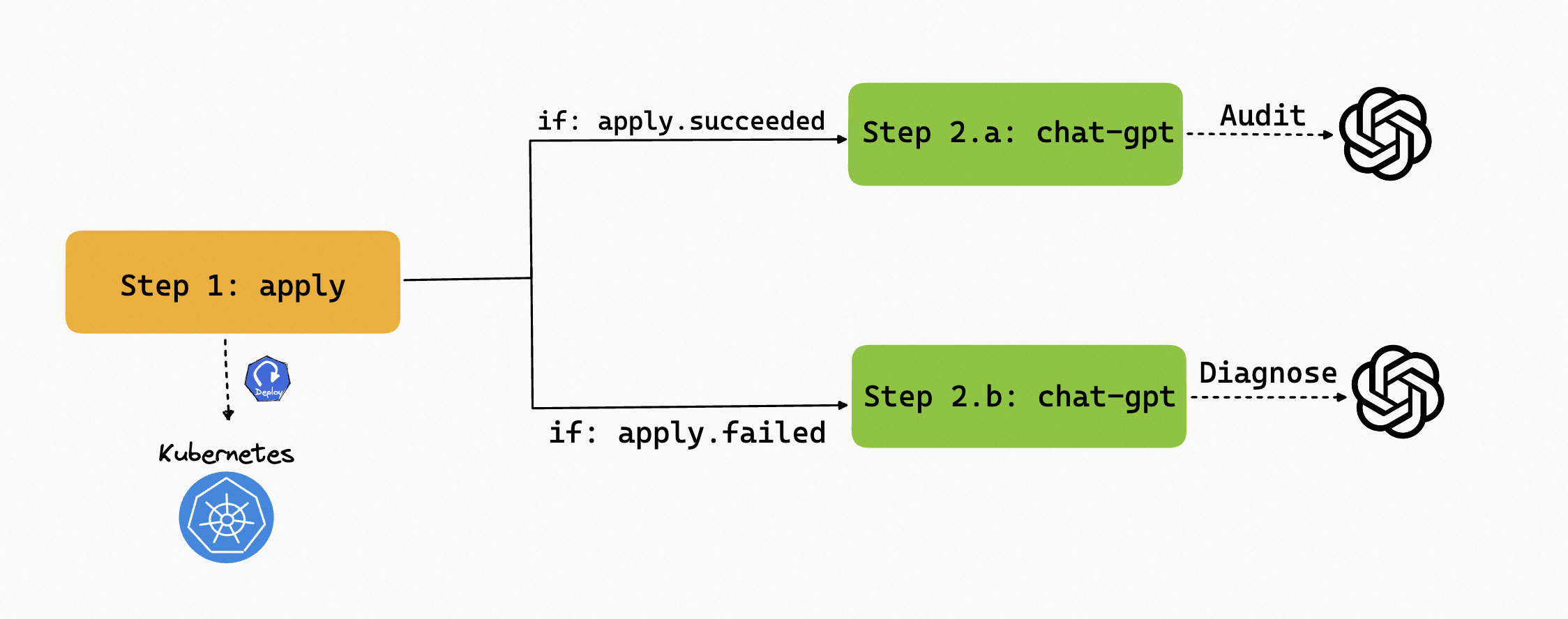
The complete Workflow is shown below:
apiVersion: core.oam.dev/v1alpha1
kind: WorkflowRun
metadata:
name: chat-gpt
namespace: default
spec:
workflowSpec:
steps:
- name: apply
type: apply-deployment
outputs:
- name: resource
valueFrom: output.value
properties:
image: nginx
# if the apply step fails, then diagnose the resource
- name: chat-diagnose
if: status.apply.failed
type: chat-gpt
inputs:
- from: resource
parameterKey: prompt.content
properties:
token:
value: <your token>
prompt:
type: diagnose
# if the apply step succeeds, then audit the resource
- name: chat-audit
if: status.apply.succeeded
type: chat-gpt
inputs:
- from: resource
parameterKey: prompt.content
properties:
token:
value: <your token>
prompt:
type: audit
Case 3: Use ChatGPT as a quality gate
If we want to apply the resources to a production environment, can we let ChatGPT rate the quality of the resource first, only if the quality is high enough, then apply the resource to the production environment? Absolutely!
Note that to make the score evaluated by chat-gpt more convincing, it's better to pass metrics than the resource in this case.
Let's write our Workflow. KubeVela Workflow has the capability to apply resources to multi clusters. The first step is to apply the Deployment to the test environment. The second step is to use the ChatGPT to rate the quality of the resource. If the quality is high enough, then apply the resource to the production environment.
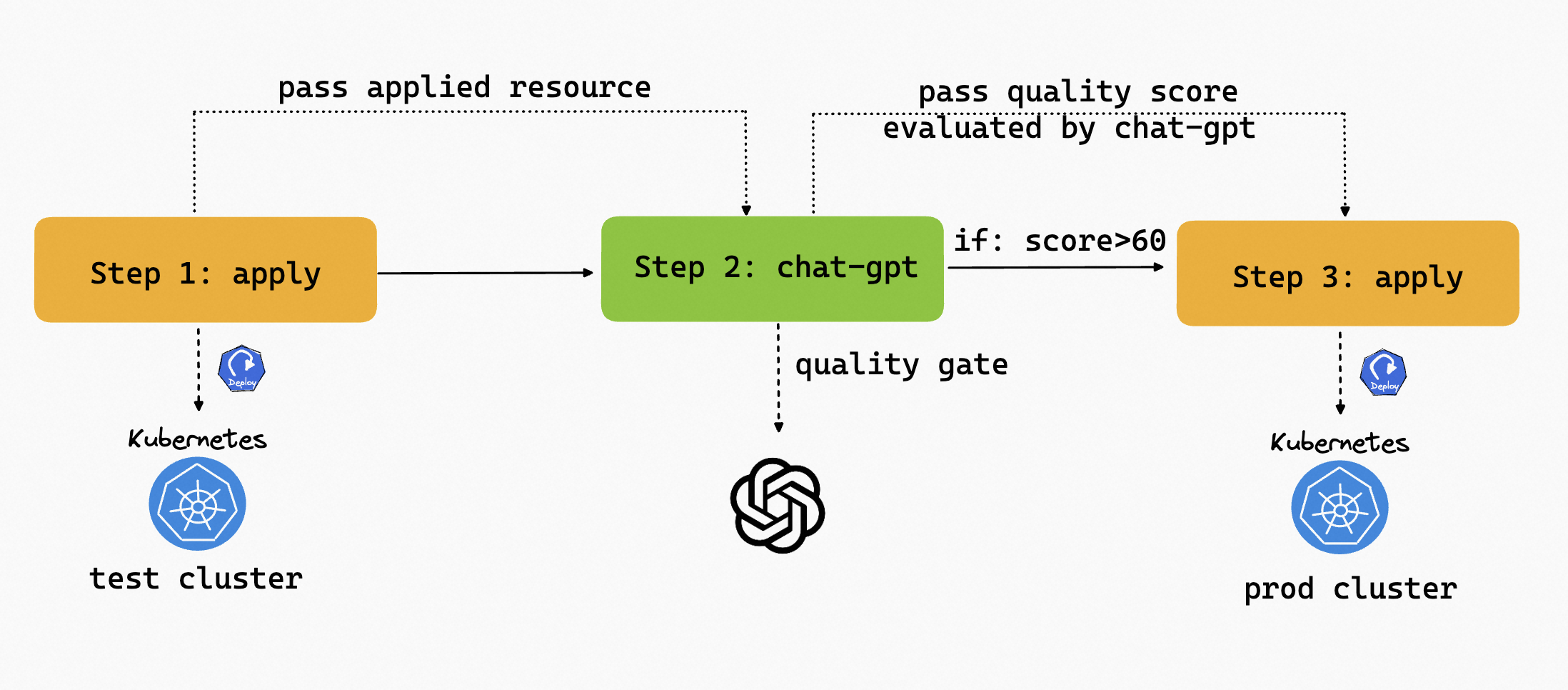
The complete Workflow is shown below:
apiVersion: core.oam.dev/v1alpha1
kind: WorkflowRun
metadata:
name: chat-gpt-quality-gate
namespace: default
spec:
workflowSpec:
steps:
# apply the resource to the test environment
- name: apply
type: apply-deployment
# output the resource to the next step
outputs:
- name: resource
valueFrom: output.value
properties:
image: nginx
cluster: test
- name: chat-quality-check
# this step will always be executed
if: always
type: chat-gpt
# get the inputs from resource and pass it to the prompt.content
inputs:
- from: resource
parameterKey: prompt.content
# output the score of ChatGPT and use strconv.Atoi to convert the score string to int
outputs:
- name: chat-result
valueFrom: |
import "strconv"
strconv.Atoi(result)
properties:
token:
value: <your token>
prompt:
type: quality-gate
# if the score is higher than 60, then apply the resource to the production environment
- name: apply-production
type: apply-deployment
# get the score from chat-result
inputs:
- from: chat-result
# check if the score is higher than 60
if: inputs["chat-result"] > 60
properties:
image: nginx
cluster: prod
Apply this Workflow and we can see that if the score is higher than 60, then the resource will be applied to the production environment.
In the End
ChatGPT brings imagination to the world of Kubernetes. Diagnose, audit, rate is just the beginning. In the new AI era, the most precious thing is idea. What do you want to do with ChatGPT? Share your insights with us in the KubeVela Community.